To connect multiple solar inverters together, you need to ensure the inverters are compatible, follow precise steps for parallel or series connections, and verify all safety and electrical requirements. Properly connected inverters can enhance your solar power system’s capacity and efficiency.
Let’s explore the details and best practices for connecting multiple solar inverters together.
Why Connect Multiple Solar Inverters?
Connecting multiple solar inverters is often necessary for various practical and strategic reasons.
First and foremost, scaling up capacity is a key driver. As energy demands increase, especially in large installations, adding more inverters allows the integration of additional solar panels, thereby significantly boosting the system’s overall energy output. This scalability ensures that the system can meet growing energy needs over time.
Another crucial reason is redundancy. In large-scale solar power systems, having multiple inverters creates a fail-safe mechanism. If one inverter experiences a fault or failure, the other inverters can continue operating, ensuring that the system remains functional and energy production is not entirely halted. This redundancy minimizes downtime and ensures a more reliable power supply.
Finally, multiple inverters enable optimizing energy distribution. In complex systems where energy loads vary or need to be distributed across different locations, multiple inverters can manage and balance the energy flow more effectively, ensuring that each part of the system receives the appropriate amount of power, thereby enhancing overall efficiency.
Types of Solar Inverter Configurations
When connecting multiple inverters, there are different configurations to consider, each offering specific benefits:
1. Parallel Connection
In a parallel configuration, the AC output from multiple inverters is combined to boost the overall power output. This setup is common in grid-tied solar systems, especially where high energy demands are present. By paralleling inverters, the system can handle larger loads, making it ideal for commercial and industrial applications where consistent power is essential.
2. Series Connection
In a series connection, inverters are linked to increase the system’s overall voltage. This configuration is less common in standard solar setups but can be beneficial in scenarios requiring higher voltage, such as systems designed for long-distance power transmission or specific high-voltage equipment. Series connections can also reduce the current load, potentially lowering cabling costs.
3. Hybrid Systems
Hybrid configurations combine both series and parallel connections, offering flexibility in system design. These systems are useful in complex installations with varying energy needs or where the system must accommodate both grid-tied and off-grid scenarios, optimizing performance and reliability.
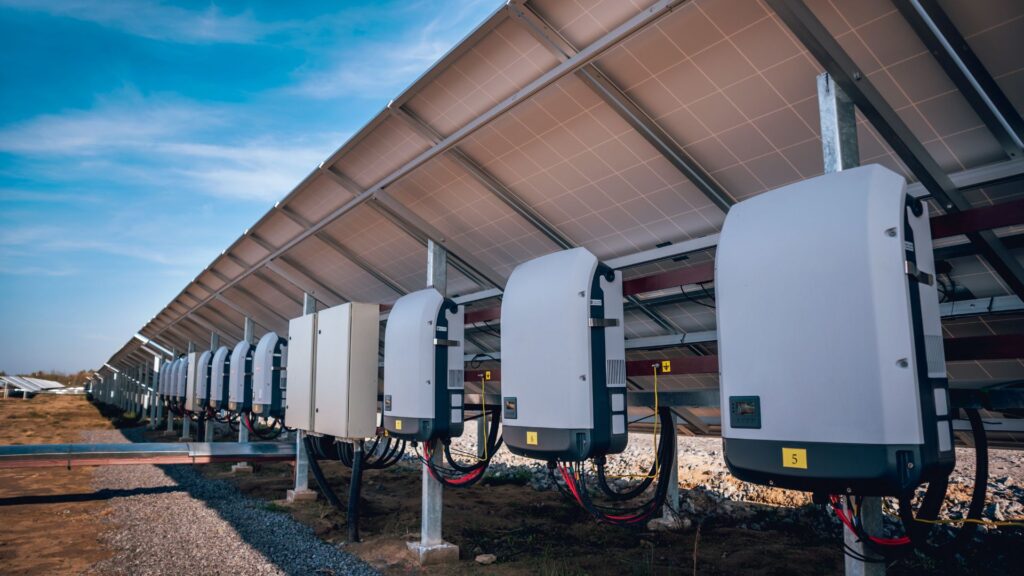

Steps to Connect Multiple Solar Inverters
Step 1: Prepare the Installation Site
Ensure that the installation site is fully prepared to accommodate multiple inverters. This preparation involves several key aspects:
- Adequate Space: Confirm that there is sufficient physical space to house all the inverters, ensuring proper clearance around each unit. Adequate ventilation is crucial to prevent overheating and maintain optimal performance. Consider future expansion and ensure that the space can accommodate additional inverters if needed.
- Wiring Infrastructure: Verify that the site has the necessary wiring infrastructure in place. This includes selecting cables of appropriate gauge and insulation to manage the combined electrical output of the inverters safely. Properly plan cable routing to avoid interference, ensure safety, and maintain system efficiency.
Step 2: Install the Solar Inverters
Mount the solar inverters carefully following the manufacturer’s instructions. This process generally includes:
- Securing the inverters: Ensure each inverter is securely attached to the mounting surface to prevent vibrations or movement that could lead to damage. Proper mounting is essential for long-term stability and performance.
- Proper Grounding: Ground each inverter as specified in the installation manual. Proper grounding is critical for safety, protecting the system from electrical faults, and ensuring compliance with electrical codes.
Step 3: Connect the Inverters
The connection process varies based on the configuration—parallel or series:
- Parallel Connection:
1) DC Connection: Connect the DC input from the solar panels to the DC input terminals on each inverter. Ensure secure connections and that wiring is appropriately sized for the combined current.
2) AC Output: Connect the AC outputs of each inverter together using a combiner box or parallel connection kit. This merges the outputs into a single AC output. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure a safe, efficient connection.
3) Grid or Load Connection: Depending on your system design, the combined AC output is then connected to the main distribution panel or directly to the grid. Proper synchronization with the grid is crucial for stable operation.
- Series Connection:
1) DC Connection: Connect the DC output from one inverter to the DC input of the next in a series, continuing until all inverters are linked. Ensure the voltage is within the inverters’ specifications.
2) AC Output: The final inverter in the series will provide the AC output, which can be connected to the grid or a designated load as required. Ensure all connections are secure and that the system’s voltage matches the grid or load requirements.
Step 4: Test the System
Once all connections are made, it’s essential to test the system thoroughly:
- Power On: Begin by turning on each inverter individually, ensuring they power up correctly without any error messages. Verify that each inverter is operational and ready for synchronization.
- Synchronization: In grid-tied systems, carefully check that each inverter synchronizes properly with the grid’s frequency and voltage. This step is crucial to ensure the system functions harmoniously with the grid and avoids potential disruptions.
- Monitoring: Use monitoring tools or software to assess each inverter’s output. Ensure that all inverters operate efficiently, within their specified parameters, and produce the expected energy output. This step helps identify any issues early and ensures optimal system performance.
Step 5: Safety Checks and Final Inspection
Before commissioning the system, conduct comprehensive safety checks:
- Electrical Safety: Carefully inspect all connections to ensure they are secure, with no loose wires or exposed conductors that could lead to electrical hazards. Address any issues immediately to prevent potential risks.
- Overload Protection: Install appropriate circuit breakers or fuses to safeguard the system against overloads. These protective devices are crucial for preventing damage to the inverters and ensuring the system operates safely under all conditions.
- Regulatory Compliance: Verify that the entire system complies with local electrical codes and standards. It’s often necessary to have the system inspected by a certified electrician or local authority to ensure it meets all regulatory requirements and is safe for operation.

Common Challenges and Troubleshooting
Connecting multiple solar inverters can present several challenges. Understanding these potential issues and how to address them is crucial for a successful installation.
1. Inverter Compatibility Issues
If inverters are incompatible, they may fail to sync correctly, leading to inefficiencies or potential damage. Always check compatibility, including voltage ratings and communication protocols, before purchasing or installing inverters to ensure they can work together seamlessly.
2. Voltage Drops
Long cable runs between inverters can cause voltage drops, reducing system efficiency. To minimize this, use appropriately sized cables that can handle the current and keep the distance between inverters as short as possible to maintain optimal performance.
3. Synchronization Problems
In grid-tied systems, inverters must synchronize with the grid’s frequency and voltage. Failure to do so can cause the system to shut down. Ensure all inverters are designed for grid connection and correctly configured to sync with the grid.
4. Overheating
Multiple inverters in close proximity can generate excessive heat, leading to overheating issues. Ensure adequate ventilation around the inverters, and consider installing cooling systems such as fans if necessary to prevent heat buildup and maintain system reliability.
Maintenance and Monitoring
Regular maintenance is essential for the long-term performance of a system with multiple solar inverters:
- Routine Inspections: Periodically inspect all connections, wiring, and inverters for any signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Early detection of issues can prevent more significant problems down the line.
- Cleaning: Keep the inverters clean and free from dust, debris, and dirt, which can cause overheating and reduce efficiency. Regular cleaning ensures the inverters operate at optimal levels.
- Monitoring Systems: Utilize inverter monitoring systems to continuously track the performance of each inverter. These tools help identify potential issues early, allowing for timely interventions and ensuring the system runs efficiently and reliably over time.

Conclusion
Connecting multiple solar inverters together can be a complex task, but with careful planning and attention to detail, it can be done efficiently and safely. By understanding the different configurations, following the proper steps, and being aware of potential challenges, you can ensure that your solar power system operates at peak performance, providing reliable and sustainable energy for years to come.
FAQs
1. What are the benefits of connecting multiple solar inverters?
Connecting multiple solar inverters provides scalability, redundancy, and better energy distribution. It allows for the expansion of solar systems, improves reliability, and optimizes the power distribution across various loads.
2. What are the risks of connecting multiple inverters incorrectly?
Incorrectly connecting multiple inverters can lead to system inefficiencies, equipment damage, synchronization issues, and safety hazards. It’s vital to follow proper installation procedures and check compatibility before connecting inverters.
3. What should I consider when planning to connect multiple solar inverters?
When planning to connect multiple solar inverters, consider system design, load calculation, inverter compatibility, and whether your system is grid-tied or off-grid. Ensure compliance with local regulations and standards to guarantee safe and efficient operation.
4. Do you need special equipment to connect multiple inverters?
Yes, depending on the configuration, you may need special equipment like combiner boxes, parallel connection kits, or synchronization devices to safely and efficiently connect multiple inverters.
5. Can you mix different brands of solar inverters in the same system?
Mixing different brands of inverters is generally not recommended because they may have different operating characteristics, which can lead to synchronization issues and reduced system performance. Always check compatibility before mixing brands.
6. How do you handle voltage drops when connecting multiple inverters?
To handle voltage drops, use appropriately sized cables and minimize the distance between inverters. Ensuring proper cable sizing and connection quality is essential to maintain system efficiency.